pipeline
官方文档:
https://www.jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/steps/workflow-basic-steps/#wrap-general-build-wrapper
https://www.jenkins.io/zh/node/
https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/pipeline/syntax/#declarative-pipeline
中文文档,https://www.jenkins.io/zh/doc/pipeline/tour/getting-started/
https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/pipeline/syntax/
查看内置变量
可以参考,https://52wiki.cn/project-14/doc-616/
Jenkins从根本上说是一个支持多种自动化模式的自动化引擎。Pipeline在Jenkins上增加了一套强大的自动化工具,支持从简单的持续集成到全面的CD管道的用例。通过对一系列相关任务建模,用户可以利用Pipeline的更多功能,如:
- 可维护:管道是在代码中实现的,并且通常会被签入源代码管理,从而使团队能够编辑,审阅和迭代他们的交付管道。
- 可能出现:在继续进行管道运行之前,管道可以选择停止并等待人员输入或批准。
- 复杂场景:管道支持复杂的实际CD需求,包括分叉/连接,循环和并行执行工作的能力。
- 可扩展性:Pipeline插件支持对其DSL的定制扩展
1.1 创建
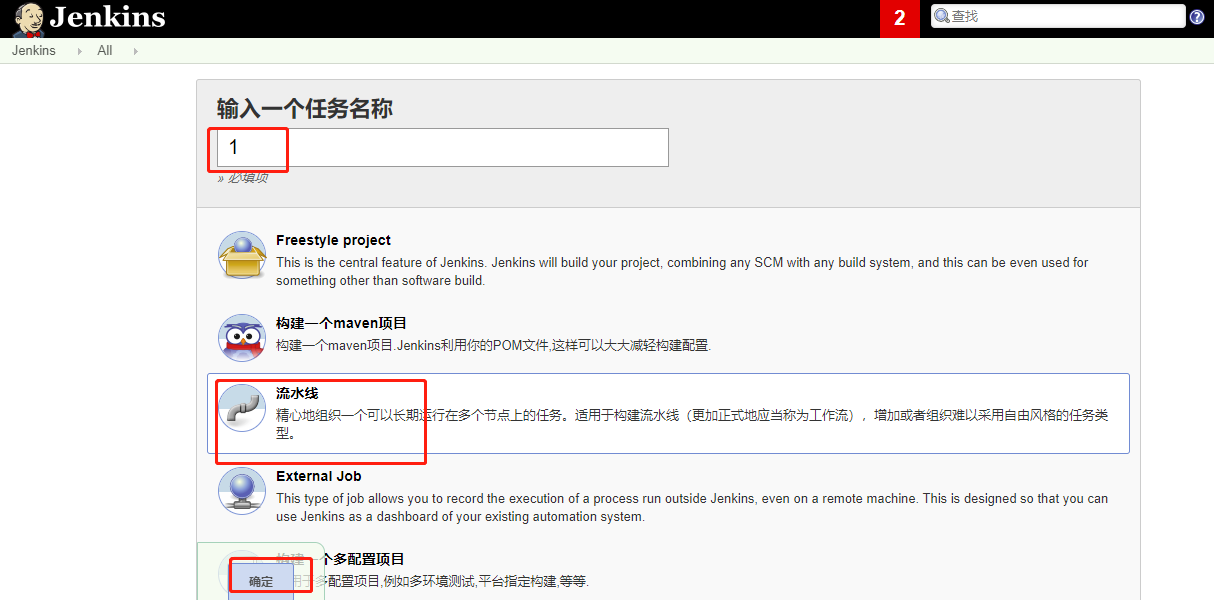
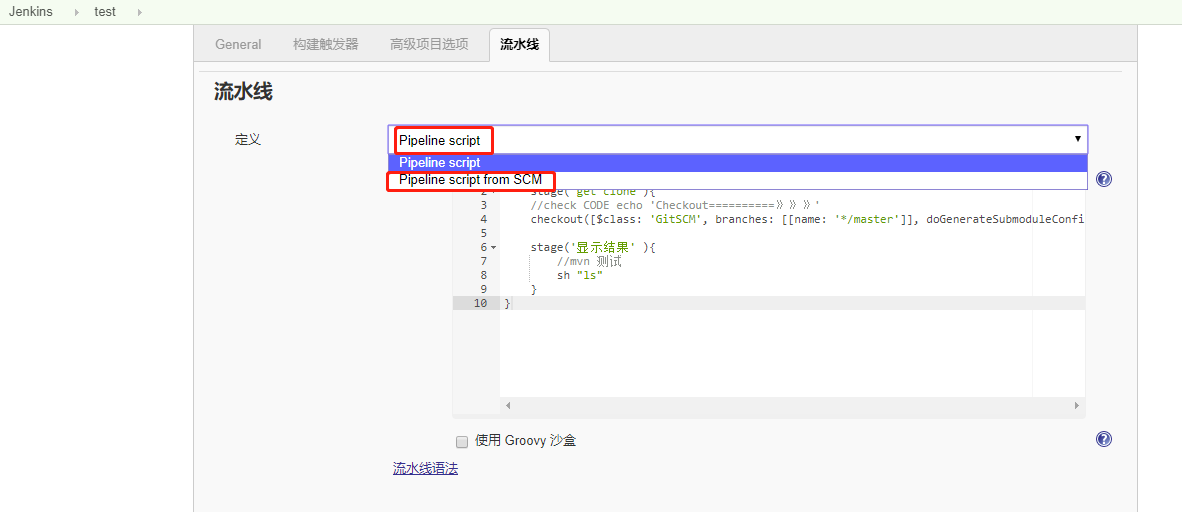
1.2 pipeline script
Script模式
Scripted Pipeline则是旧版本中 Jenkins 支持的 Pipeline 模式,主要是写一些 groovy 的代码来制定流程
简单案例
node {
stage('Build'){
println "Build"
}
stage('Test'){
println "Test"
}
stage('Deploy'){
println "Deploy"
}
}
#脚本化的流水线自由度更高,因此我们选择脚本的写法node {
stage('Build'){
println "Build"
}
stage('Test'){
println "Test"
}
stage('Deploy'){
println "Deploy"
}
}
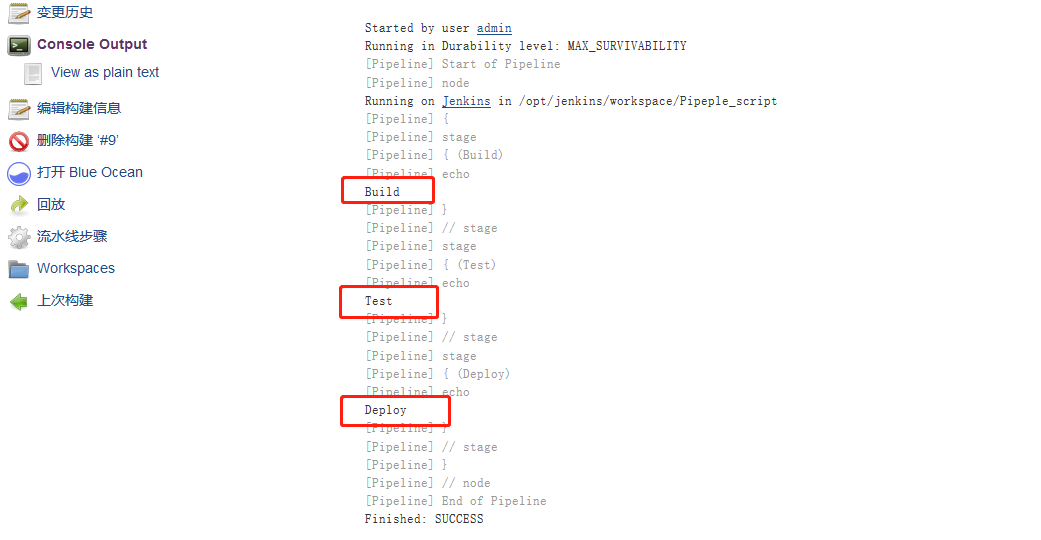
#脚本化的流水线自由度更高,因此我们选择脚本的写法- 效果图
Declarative类型
Declarative Pipeline
Declarative Pipeline 最外层有个 pipeline 表明它是一个声明式流水线,下面会有 4 个主要的部分: agent,post,stages,stepsDeclarative Pipeline 最外层有个 pipeline 表明它是一个声明式流水线,下面会有 4 个主要的部分: agent,post,stages,stepsAgent
agent 主要用于描述整个 Pipeline 或者指定的 Stage 由什么规则来选择节点执行。Pipeline 级别的 agent 可以视为 Stage 级别的默认值,如果 stage 中没有指定,将会使用与 Pipeline 一致的规则。在最新的 Jenkins 版本中,可以支持指定任意节点(any),不指定(none),标签(label),节点(node),docker,dockerfile 和 kubernetes 等,具体的配置细节可以查看文档
Tips:
- 如果 Pipeline 选择了 none,那么 stage 必须要指定一个有效的 agent,否则无法执行
- Jenkins 总是会使用 master 来执行 scan multibranch 之类的操作,即使 master 配置了 0 executors
- agent 指定的是规则而不是具体的节点,如果 stage 各自配置了自己的 agent,需要注意是不是在同一个节点执行的
Stages && Stage
Stages 是 Pipeline 中最主要的组成部分,Jenkins 将会按照 Stages 中描述的顺序从上往下的执行。Stages 中可以包括任意多个 Stage,而 Stage 与 Stages 又能互相嵌套,除此以外还有 parallel 指令可以让内部的 Stage 并行运行。实际上可以把 Stage 当作最小单元,Stages 指定的是顺序运行,而 parallel 指定的是并行运行
pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Sequential') {
stages {
stage('In Sequential 1') {
steps {
echo "In Sequential 1"
}
}
stage('In Sequential 2') {
steps {
echo "In Sequential 2"
}
}
stage('Parallel In Sequential') {
parallel {
stage('In Parallel 1') {
steps {
echo "In Parallel 1"
}
}
stage('In Parallel 2') {
steps {
echo "In Parallel 2"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Sequential') {
stages {
stage('In Sequential 1') {
steps {
echo "In Sequential 1"
}
}
stage('In Sequential 2') {
steps {
echo "In Sequential 2"
}
}
stage('Parallel In Sequential') {
parallel {
stage('In Parallel 1') {
steps {
echo "In Parallel 1"
}
}
stage('In Parallel 2') {
steps {
echo "In Parallel 2"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}Steps
steps 是 Pipeline 中最核心的部分,每个 Stage 都需要指定 Steps。Steps 内部可以执行一系列的操作,任意操作执行出错都会返回错误。完整的 Steps 操作列表可以参考 Pipeline Steps Reference,这里只说一些使用时需要注意的点。
- groovy 语法中有不同的字符串类型,其中
'abc'是 Plain 字符串,不会转义${WROKSPACE}这样的变量,而"abc"会做这样的转换。此外还有''' xxx '''支持跨行字符串,"""同理。 - 调用函数的
()可以省略,使得函数调用形如updateGitlabCommitStatus name: 'build', state: 'success',通过,来分割不同的参数,支持换行。 - 可以在声明式流水线中通过
script来插入一段 groovy 脚本
Post
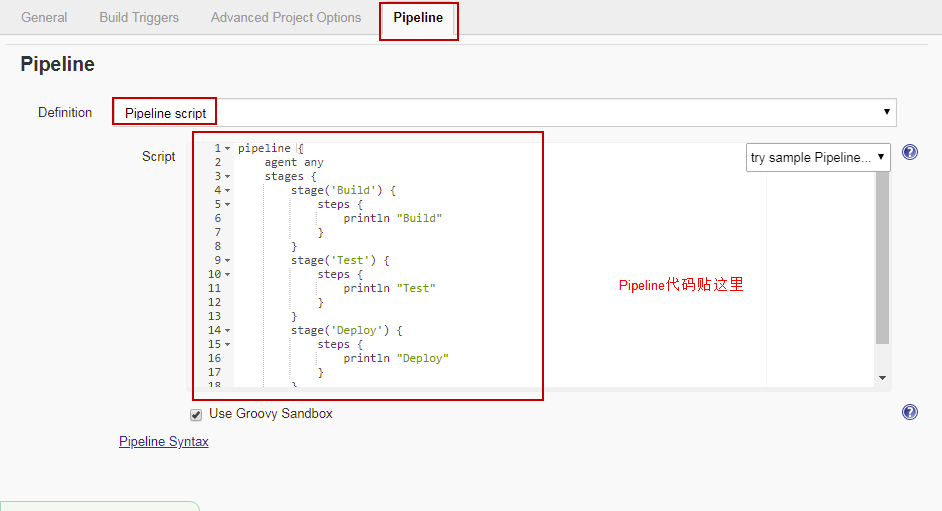
post 部分将会在 pipeline 的最后执行,经常用于一些测试完毕后的清理和通知操作。文档中给出了一系列的情况,比较常用的是 always,success 和 failurepost 部分将会在 pipeline 的最后执行,经常用于一些测试完毕后的清理和通知操作。文档中给出了一系列的情况,比较常用的是 always,success 和 failurepipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
println "Build"
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
println "Test"
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
println "Deploy"
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
println "Build"
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
println "Test"
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
println "Deploy"
}
}
}
}
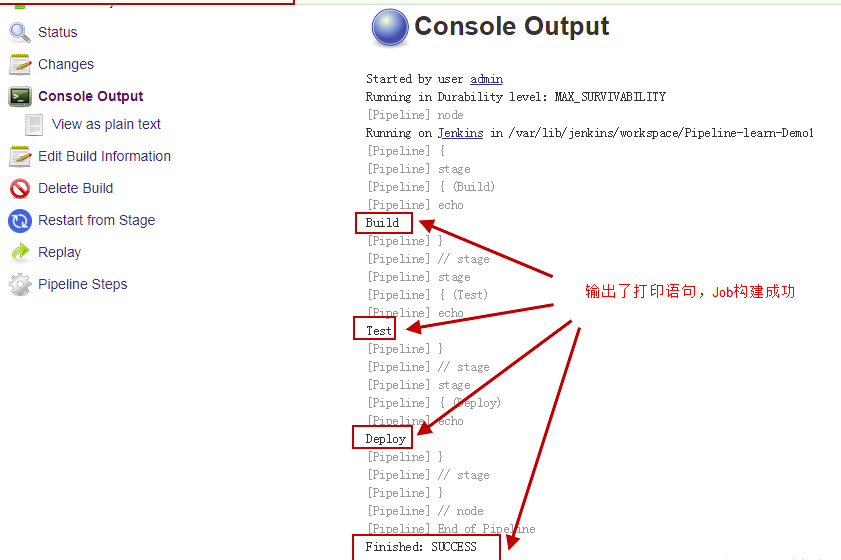
其中关键语法异同如下:
- pipeline 是声明性管道特定语法,它定义了一个包含执行整个管道的所有内容和指令的“块”。
- agent 是声明式管道特定的语法,它指示Jenkins为整个管道分配执行程序(在节点上)和工作空间。
- stage是描述此Pipeline阶段的语法块 。stage在Pipeline语法页面上阅读关于声明式管道语法块的更多信息。如所提到的上述,stage块在脚本管道语法可选的。
- steps是声明式管道特定语法,用于描述要在此中运行的步骤stage。
- sh是一个Pipeline 步骤(由 Pipeline:Nodes和Processes插件提供)执行给定的shell命令。
- node是脚本化的管道特定语法,指示Jenkins在任何可用的代理/节点上执行此管道(以及其中包含的任何阶段)。这与agent声明式管道特定语法中的效果相同
1.3 Jekninsfile
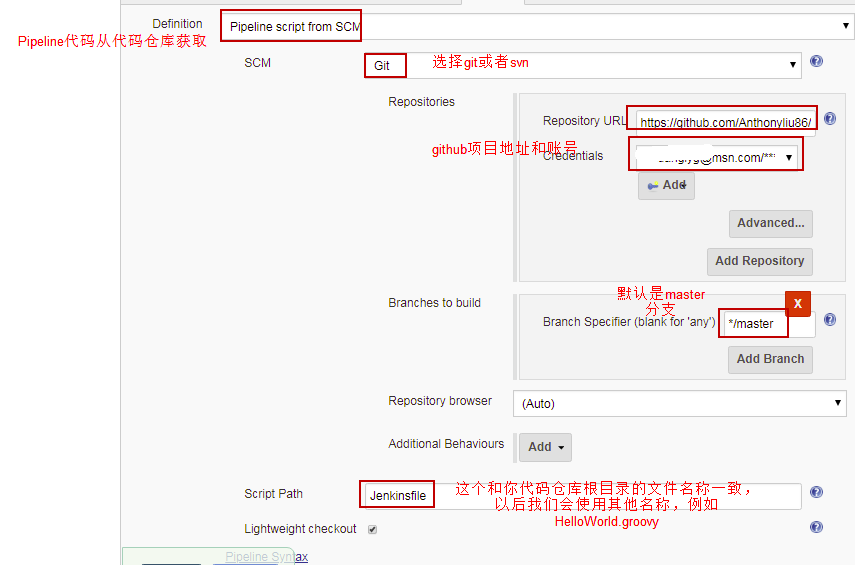
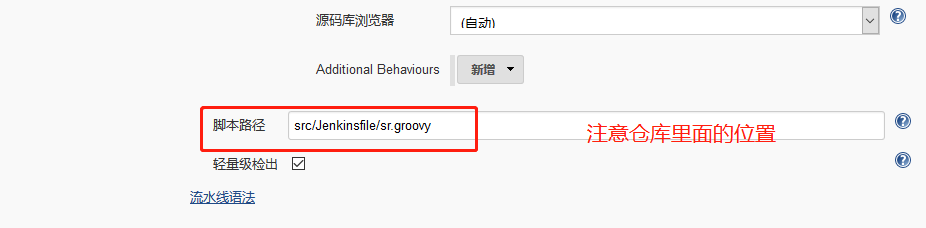
作用 直接在服务端代码仓库根目录下面添加Jenkinsfile文件,Pipeline代码放到Jenkinsfile文件中,用于描述流水线构建流程
可以用以下地址作为 测试
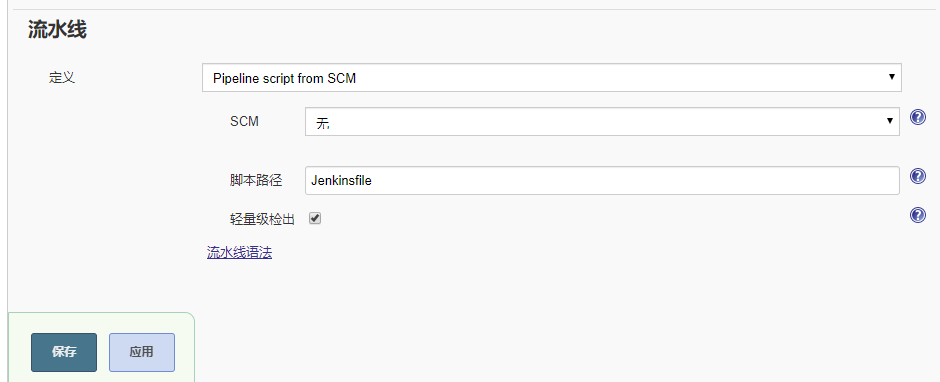
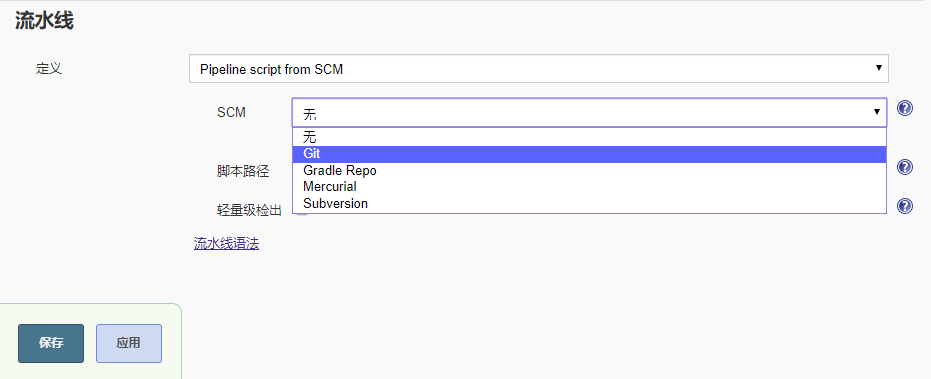
- git
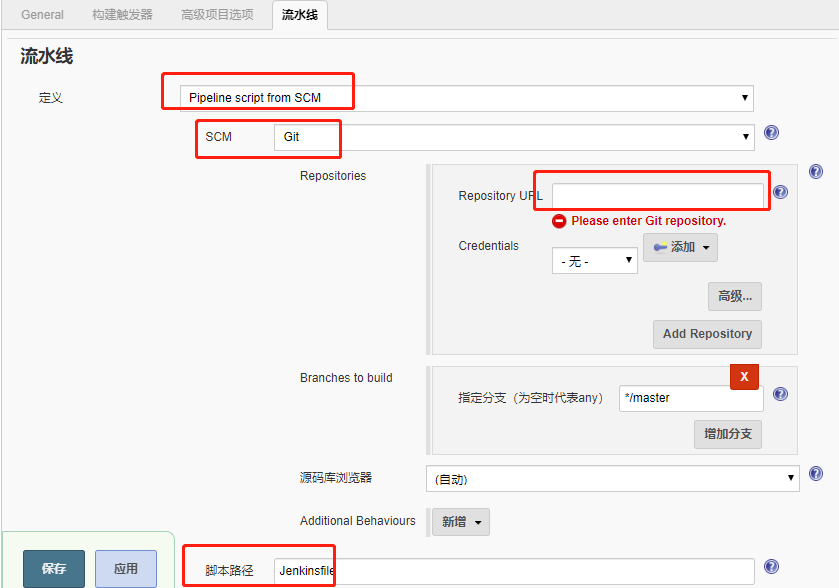
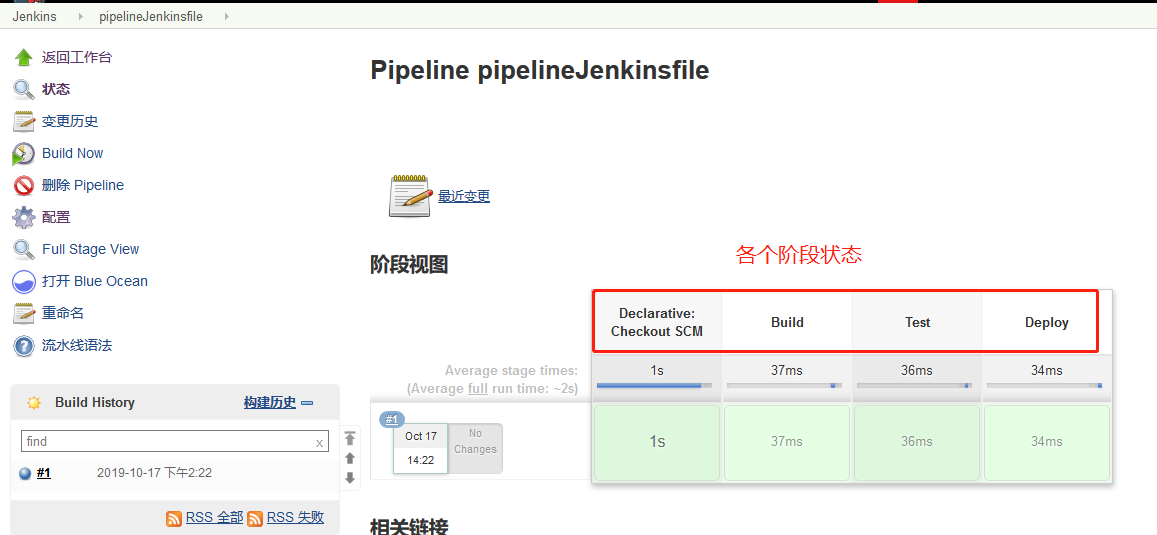
- 状态
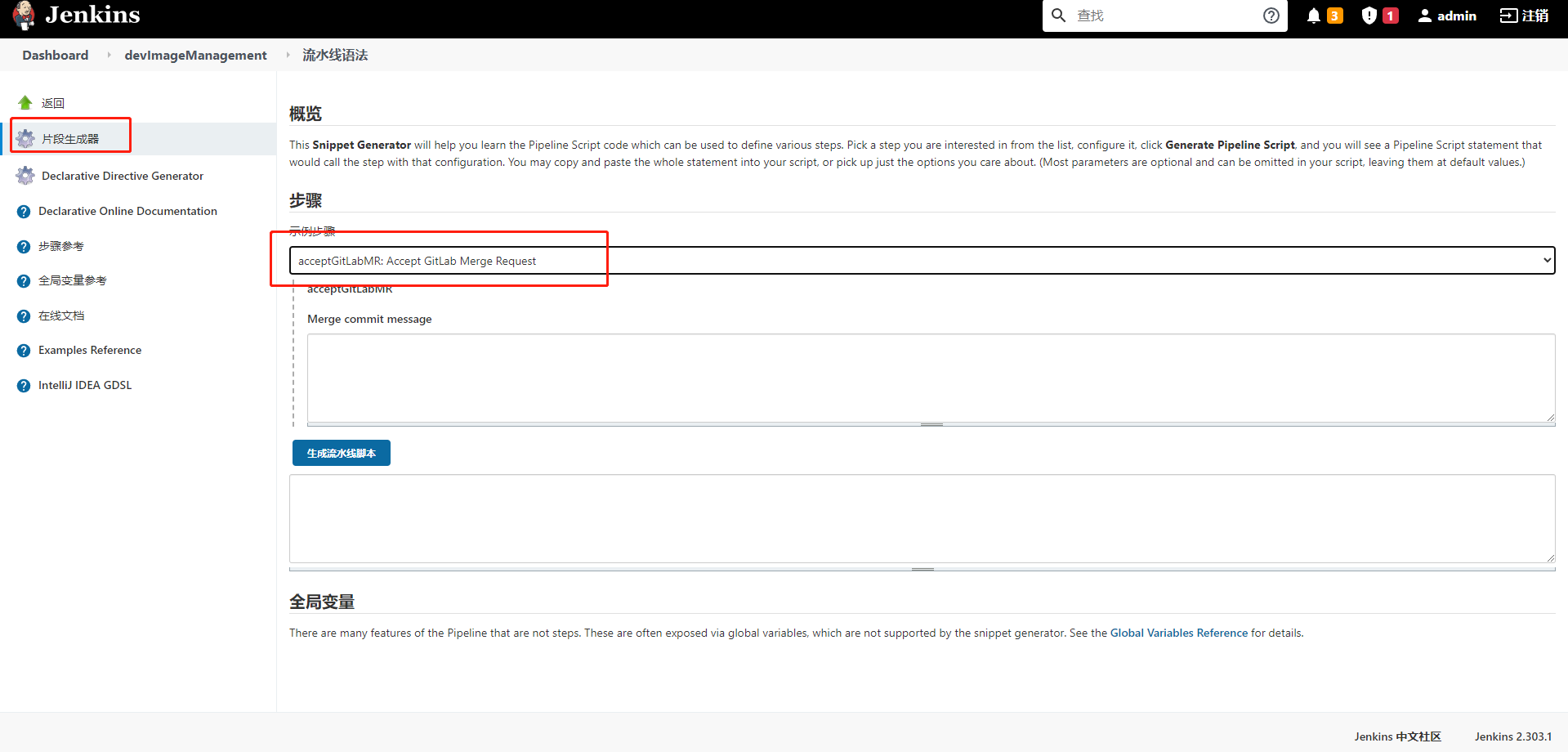
1.Pipeline 开发工具
选择任意pipeline类型的作业,点击“流水线语法”即可进入pipeline开发工具页面
1.1片段生成器
流水线代码片段生成器, 非常好用。在这里可以找到每个插件以及Jenkins内置的方法的使用方法。使用片段生成器可以根据个人需要生成方法,有些方法来源于插件,则需要先安装相关的插件才能使用
1.2声明式语法生成器
可以生成声明式流水线语法的语句块
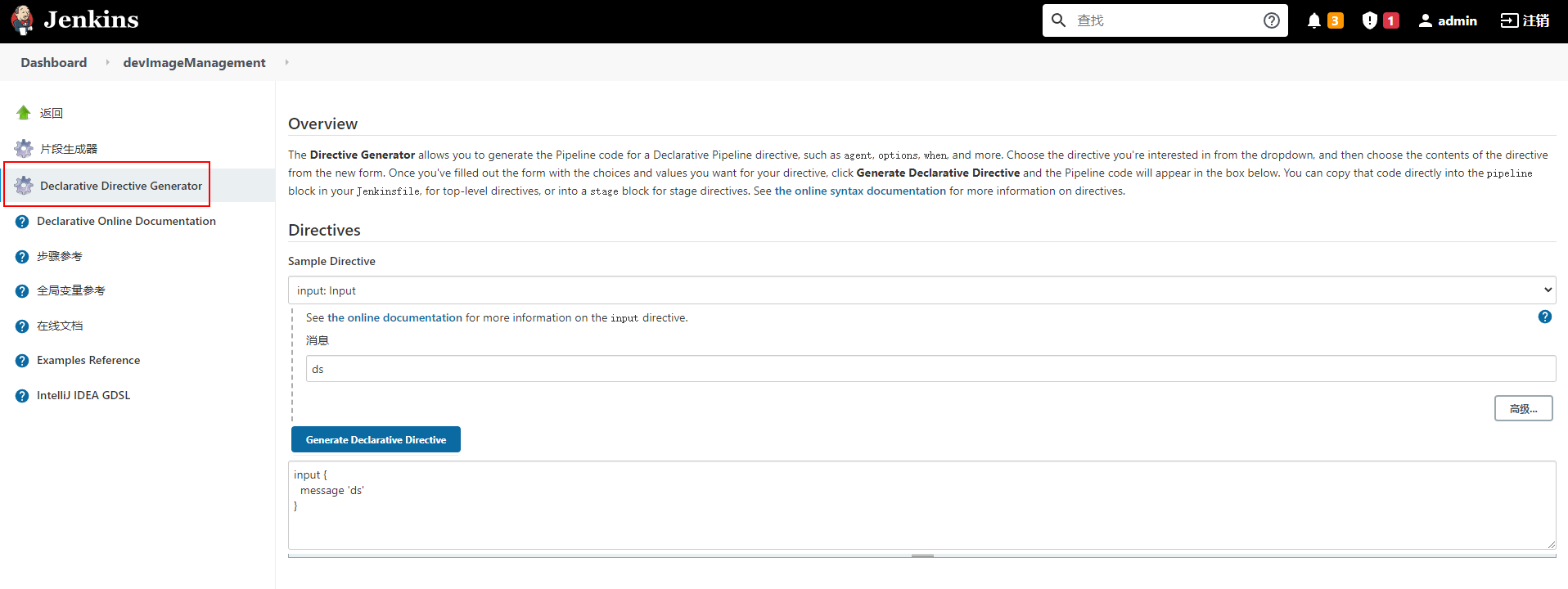
1.3生成语法
- Declarative Pipeline 脚本生成器 http://JENKINS_ROOT/directive-generator/
- Script Pipeline 脚本生成器 http://JENKINS_ROOT/pipeline-syntax/
入口在上边配置工程的最下边,如图 流水线语法
- 流水线语法使用示意

2.基本语法
2.0stages
- 关系: stages > stage > steps > script
- 定义
○ stages:包含多个stage阶段 ○ stage: 包含多个steps步骤 ○ steps: 包含一组特定的脚本(加上script后就可以实现在声明式脚本中嵌入脚本式语法了)
- 案例
#在声明式语法中可以嵌入脚本式语法:
pipeline{
agent{label "build"}
stages{
stage('echo the rr'){
steps{
script{
a = 1
println("${a}")
}
}
}
}
}#在声明式语法中可以嵌入脚本式语法:
pipeline{
agent{label "build"}
stages{
stage('echo the rr'){
steps{
script{
a = 1
println("${a}")
}
}
}
}
}基本语法:
一个pipeline中只能包含一个stages
一个stages可以包含多个stage('xxx')
一个stage('xxx')可以包含一个steps
2.1预设指令
各种预设指令(Directive)的从属关系如下:图中,实线框表示必选模块,虚线框表示可选模块

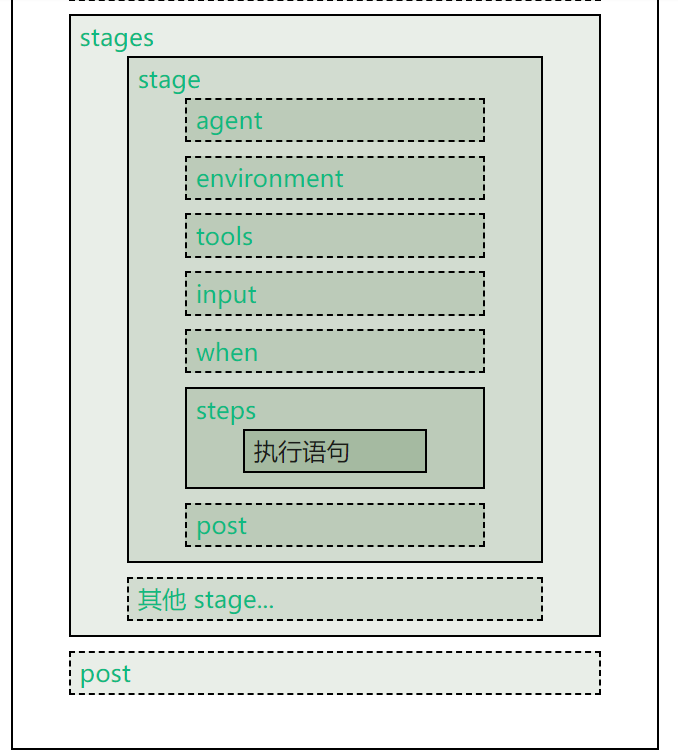
2.2 agent
agent 指令用于指定所在模块(pipeline、stage)的运行环境,可以是Jenkins 节点机或者 docker 容器
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| any | 在任何可用的节点上执行pipeline |
| none | 没有指定agent的时候默认 |
| label | 在指定标签上的节点运行pipeline |
| node | 支持自定义流水线的工作目录 |
#在任一节点运行
agent any
#标签选择
agent { label "label Name" }
#自定义节点、工作目录
agent {
node {
label "labelName",
customWorkspace "/opt/agent/workspace"
}
}#在任一节点运行
agent any
#标签选择
agent { label "label Name" }
#自定义节点、工作目录
agent {
node {
label "labelName",
customWorkspace "/opt/agent/workspace"
}
}2.3 environment
$变量名 environment文档
指定所在模块(pipeline、stage)的环境变量, key = value 的形式。Job 的参数,需要通过 environment 环境变量的方式 ${params.xxxx} 传递给执行脚本,分为==全局级别(流水线级别)和阶段级别==
- 全局级别
pipeline {
environment {
USER = 'username'
PASSWORD = 'xxxxxx'
type = "${params.type}"
}
}pipeline {
environment {
USER = 'username'
PASSWORD = 'xxxxxx'
type = "${params.type}"
}
}- 阶段级别
pipeline {
...
...
stages {
stage("build"){
environment {
VERSION = "1.1.20"
}
steps {
script {
echo "${VERSION}"
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
...
...
stages {
stage("build"){
environment {
VERSION = "1.1.20"
}
steps {
script {
echo "${VERSION}"
}
}
}
}
}==当全局变量和阶段变量冲突时,全局会覆盖阶段的变量==
2.4 triggers
流水线的触发方式
- cron 定时触发:
triggers { cron('H */7 * * 1-5') } - pollSCM:
triggers { pollSCM('H */7 * * 1-5') }
- cron 定时触发:
指定如何触发 Pipeline ,这个选项里以时间条件触发最为常用:
triggers {
cron('H */4 * * 1-5')
}triggers {
cron('H */4 * * 1-5')
}crontab 的写法(用 H 代替 0)和设置页面上的一致。其实最方便的还是从界面上设置
pipeline{
agent{ label "build"}
triggers {
cron '*/1 * * * *'
//cron('H */7 * * 1-5')
}
stages{
stage("lovely"){
options{
timestamps()
}
steps{
echo "lovely"
}
}
}
}pipeline{
agent{ label "build"}
triggers {
cron '*/1 * * * *'
//cron('H */7 * * 1-5')
}
stages{
stage("lovely"){
options{
timestamps()
}
steps{
echo "lovely"
}
}
}
}2.5 libraries
由于 Declarative Pipeline 的声明格式比较固定,如果有需要重复执行的语句片段,需要抽象为函数,就难以支持。可以使用 Shared Libraries 将共同的语句提取出来
其实如果是简单的逻辑,可以使用Scripted Pipeline 实现
2.6 options
options指令允许从流水线内部配置特定于流水线的选项。流水线提供了许多这样的选项,比如buildDiscarder,也可以有插件提供,比如timestamps
Pipeline配置参数
| 参数名 | 说明 | 例子 |
|---|---|---|
| buildDiscarder | 保留最近历史构建记录的数量 | buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr: '10') |
| checkoutToSubdirectory | 将代码从版本控制库中拉取后,保存在工作目录的子目录 | checkoutToSubdirectory('subdir') |
| disableConcurrentBuilds | 禁用Jenkins同时执行多次该pipeline | disableConcurrentBuilds() |
| newContainerPerStage | agent为Docker或Dockerfile时,每个stage都分别运行在一个新容器中 | newContainerPerStage() |
| retry | pipeline发生失败后重试次数 | retry(4) |
| timeout | pipeline运行超时时间 | timeout(time:10, unit: 'HOURS/MINUTES') |
| overridenIndexTriggers | 允许覆盖分支索引触发器的默认处理 | |
| skipDefaultCheckout | 在agent指令中,跳过从源代码控制中检出代码的默认情况 |
## 设置保存最近的记录
options { buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr: '1')) }
## 禁止并行构建
options { disableConcurrentBuilds() }
## 跳过默认的代码检出
options { skipDefaultCheckout() }
## 设定流水线的超时时间(可用于阶段级别)
options { timeout(time: 1, unit: 'HOURS') }
## 设定流水线的重试次数(可用于阶段级别)
options { retry(3) }
## 设置日志时间输出(可用于阶段级别)
options { timestamps() }
## 设置保存最近的记录
options { buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr: '1')) }
## 禁止并行构建
options { disableConcurrentBuilds() }
## 跳过默认的代码检出
options { skipDefaultCheckout() }
## 设定流水线的超时时间(可用于阶段级别)
options { timeout(time: 1, unit: 'HOURS') }
## 设定流水线的重试次数(可用于阶段级别)
options { retry(3) }
## 设置日志时间输出(可用于阶段级别)
options { timestamps() }LogRotator构造参数分别为:
daysToKeep: 构建记录将保存的天数
numToKeep: 最多此数目的构建记录将被保存
artifactDaysToKeep: 比此早的发布包将被删除,但构建的日志、操作历史、报告等将被保留
artifactNumToKeep: 最多此数目的构建将保留他们的发布包
options {
disableConcurrentBuilds()
skipDefaultCheckout()
buildDiscarder logRotator(artifactDaysToKeepStr: '7', artifactNumToKeepStr: '3', daysToKeepStr: '6', numToKeepStr: '6')
timeout(time: 5, unit: 'MINUTES')
retry(3)
timestamps()
}LogRotator构造参数分别为:
daysToKeep: 构建记录将保存的天数
numToKeep: 最多此数目的构建记录将被保存
artifactDaysToKeep: 比此早的发布包将被删除,但构建的日志、操作历史、报告等将被保留
artifactNumToKeep: 最多此数目的构建将保留他们的发布包
options {
disableConcurrentBuilds()
skipDefaultCheckout()
buildDiscarder logRotator(artifactDaysToKeepStr: '7', artifactNumToKeepStr: '3', daysToKeepStr: '6', numToKeepStr: '6')
timeout(time: 5, unit: 'MINUTES')
retry(3)
timestamps()
}这是所在模块(pipeline、stage)的运行参数设置,有下面一些用途:
options {
timestamps() //打开控制台日志的时间戳
retry(3) // 指定失败后的重试次数
quietPeriod(30) // 指定启动前等待的秒数
timeout(time: 1, unit: 'HOURS') // 指定任务的超时时间,超时将放弃该任务
buildDiscarder logRotator(
daysToKeepStr: '6',
numToKeepStr: '6'
)
disableConcurrentBuilds()//禁止并行构建,因为用的worksapce还是同一个
}options {
timestamps() //打开控制台日志的时间戳
retry(3) // 指定失败后的重试次数
quietPeriod(30) // 指定启动前等待的秒数
timeout(time: 1, unit: 'HOURS') // 指定任务的超时时间,超时将放弃该任务
buildDiscarder logRotator(
daysToKeepStr: '6',
numToKeepStr: '6'
)
disableConcurrentBuilds()//禁止并行构建,因为用的worksapce还是同一个
}2.7 parameters
定义: 流水线在运行时设置的参数,UI页面的参数。所有的参数都存储在params对象
这是 Job 的运行参数设置,决定 Build With Parameters 界面上的参数列表。只有当 Job 运行一次、解析一次 Jenkinsfile 以后才会更新在界面上。
在 Pipeline 文件的其他模块里,parameters 的设置以 params 对象形象出现,可以用来读取自定义的参数。各类型的参数定义如下:
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: 'Toggle this value')
choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something')
password(name: 'PASSWORD', defaultValue: 'SECRET', description: 'Enter a password')
}
stages {
stage("Build"){
steps {
echo "${params.VERSION}"
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: 'Toggle this value')
choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something')
password(name: 'PASSWORD', defaultValue: 'SECRET', description: 'Enter a password')
}
stages {
stage("Build"){
steps {
echo "${params.VERSION}"
}
}
}
}string
字符串类型参数
parameters {
string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '')
}parameters {
string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '')
}#!groovy
String workspace = "/opt/jenkins/workspace"
pipeline {
agent {
node {
lable "master" //指定运行节点
customWorkspace "${workspace}"
}
}
}#!groovy
String workspace = "/opt/jenkins/workspace"
pipeline {
agent {
node {
lable "master" //指定运行节点
customWorkspace "${workspace}"
}
}
}booleanParam
parameters {
booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: '')
}parameters {
booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: '')
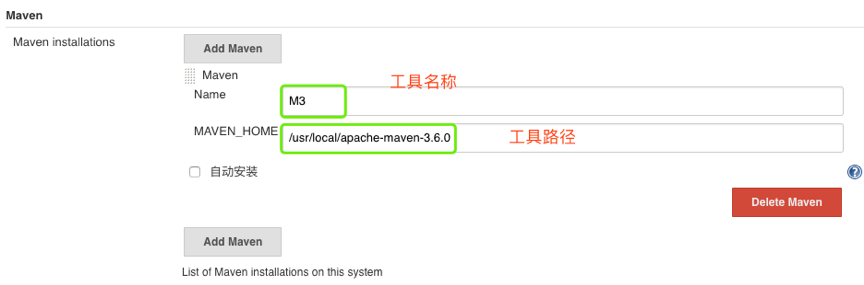
}2.8 tools
官方文档,插接件 tools文档
在 Jenkins 里 Manage Jenkins - Global Tool Configuration 里设置过的工具
获取通过自动安装或手动放置工具的环境变量。支持maven/jdk/gradle。工具的名称必须在系统设置->全局工具配置中定义
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven 'apache-maven-3.0.1'
}
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
sh 'mvn --version'
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven 'apache-maven-3.0.1'
}
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
sh 'mvn --version'
}
}
}
}- 或者
stage ("build"){
mavenHome = tool 'M3'
sh "${mavenHome}/bin/mvn -v"
}stage ("build"){
mavenHome = tool 'M3'
sh "${mavenHome}/bin/mvn -v"
}2.9 stages
stages是 pipeline 模块下的必选项,这是所有 stage 的集合,其中要包含至少一个 stage
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage ('Build') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Test') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('QA') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Deploy') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Monitor') {
echo 'hello'
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage ('Build') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Test') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('QA') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Deploy') {
echo 'hello'
}
stage ('Monitor') {
echo 'hello'
}
}
}3.0 stage
stage 真正执行语句的模块,有以下的特点:
- 每一个 stage 在 Blue Ocean 界面上对应一个圆圈;
- stage可以定义多个;
- stage 有一个必选参数,就是名称,写在 stage 后面的括号里:
stage('Example') {...} - stage 里有许多参数和 顶级 pipeline 相同
agent
如果 pipeline 中的 agent 设置为 none,则每个 stage 中必须设置 agent
environment
官方文档:https://www.jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/tour/environment/
同 pipeline 里的 environment , 规定了当前 stage 内部的环境变量。
environment指令指定一个键值对序列,该序列将被定义为所有步骤的环境变量,或者是特定于阶段的步骤,这取决于environment指令在流水线内的位置
改指令支持一个特殊的方法credentials(),该方法可用于在jenkins环境中通过标识符访问预定义的凭证。对于类型为"Secret Text"的凭证,credentials()将确保指定的环境变量包含密码文本内容。对于类型为“SStandard username and password”的凭证,指定的环境变量指定为,username:password,并且两个额外的环境变量将被自动定义:分别为MYVARNAME_USR和MYVARNAME_PSW
pipeline {
agent {
label '!windows'
}
environment {
DISABLE_AUTH = 'true'
DB_ENGINE = 'sqlite'
}
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo "Database engine is ${DB_ENGINE}"
echo "DISABLE_AUTH is ${DISABLE_AUTH}"
sh 'printenv'
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent {
label '!windows'
}
environment {
DISABLE_AUTH = 'true'
DB_ENGINE = 'sqlite'
}
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo "Database engine is ${DB_ENGINE}"
echo "DISABLE_AUTH is ${DISABLE_AUTH}"
sh 'printenv'
}
}
}
}tools
同 pipeline 里的 tools , 规定了当前 stage 内部适用的工具。
input
在 stage 开始执行前,暂停执行stage,等待用户输入信息。并不适用全自动化流水线
input用户在执行各个阶段的时候,由人工确认是否继续进行
参数:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| message | 呈现给用户的提示信息 |
| id | 可选,默认为stage名称 |
| ok | 默认表单上的ok文本 |
| submitter | 可选的,以逗号分隔的用户列表或允许提交的外部组名。默认允许任何用户 |
| submitterParameter | 环境变量的可选名称。如果存在,用submitter 名称设置 |
| parameters | 交互时用户选择的参数 |
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
input {
message "Should we continue?"
ok "Yes, we should."
submitter "alice,bob"
parameters {
string(name: 'PERSON', defaultValue: 'Mr Jenkins', description: 'Who should I say hello to?')
}
}
steps {
echo "Hello, ${PERSON}, nice to meet you."
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
input {
message "Should we continue?"
ok "Yes, we should."
submitter "alice,bob"
parameters {
string(name: 'PERSON', defaultValue: 'Mr Jenkins', description: 'Who should I say hello to?')
}
}
steps {
echo "Hello, ${PERSON}, nice to meet you."
}
}
}
}when
when 指令允许流水线根据给定的条件决定是否应该执行阶段。 when 指令必须包含至少一个条件。 如果when 指令包含多个条件, 所有的子条件必须返回True,阶段才能执行。 这与子条件在 allOf 条件下嵌套的情况相同
判断条件
- 根据环境变量判断
- 根据表达式判断
- 根据条件判断(not/allOf/anyOf)
内置条件
branch: 当正在构建的分支与模式给定的分支匹配时,执行这个阶段,这只适用于多分支流水线例如:
groovywhen { branch 'master' }when { branch 'master' }environment: 当指定的环境变量是给定的值时,执行这个步骤,例如:
groovywhen { environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' }when { environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' }expression 当指定的Groovy表达式评估为true时,执行这个阶段, 例如:
groovywhen { expression { return params.DEBUG_BUILD } }when { expression { return params.DEBUG_BUILD } }not 当嵌套条件是错误时,执行这个阶段,必须包含一个条件,例如:
groovywhen { not { branch 'master' } }when { not { branch 'master' } }allOf 当所有的嵌套条件都正确时,执行这个阶段,必须包含至少一个条件,例如:
groovywhen { allOf { branch 'master'; environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' } }when { allOf { branch 'master'; environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' } }anyOf 当至少有一个嵌套条件为真时,执行这个阶段,必须包含至少一个条件,例如:
groovywhen { anyOf { branch 'master'; branch 'staging' } }when { anyOf { branch 'master'; branch 'staging' } }
示例:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
options{
timestamps()
}
when {
branch 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
allOf {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
branch 'production'
anyOf {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'staging'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /(production|staging)/ }
anyOf {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'staging'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
agent {
label "some-label"
}
when {
beforeAgent true
branch 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
options{
timestamps()
}
when {
branch 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
allOf {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
branch 'production'
anyOf {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'staging'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /(production|staging)/ }
anyOf {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'staging'
}
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}
pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
agent {
label "some-label"
}
when {
beforeAgent true
branch 'production'
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying'
}
}
}
}条件判断(类似 if),决定所在的 stage 是否继续执行。when 的用法需要分两个维度解释:
- 语句维度:
when 里支持一些内置的判断条件,比如
when {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' // 判断环境变量
equals expected: 2, actual: currentBuild.number // 判断变量的值
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /(production|staging)/ } //Groovy布尔表达式
triggeredBy 'TimerTrigger' // 判断触发原因
branch 'master' // 多分支流水线里,判断当前所在的分支
}when {
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' // 判断环境变量
equals expected: 2, actual: currentBuild.number // 判断变量的值
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /(production|staging)/ } //Groovy布尔表达式
triggeredBy 'TimerTrigger' // 判断触发原因
branch 'master' // 多分支流水线里,判断当前所在的分支
}- 逻辑维度:
when 里的条件支持与、或、非等逻辑运算: allOf{}, anyOf{}, not{}. 它们之间可以互相嵌套至任意深度
when {
allOf {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
}when {
allOf {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
}多个条件并列默认是与关系,@allOf{}@ 可以省略,上面的例子等效于
when {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
#比如,来指定某个 Stage 指定与否:比如要配置只有在 Master 分支上才执行 push,其他分支上都只运行 build
stages {
stage('Build') {
when {
not { branch 'master' }
}
steps {
sh './scripts/run.py build'
}
}
stage('Run') {
when {
branch 'master'
}
steps {
sh './scripts/run.py push'
}
}
}when {
branch 'production'
environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production'
}
#比如,来指定某个 Stage 指定与否:比如要配置只有在 Master 分支上才执行 push,其他分支上都只运行 build
stages {
stage('Build') {
when {
not { branch 'master' }
}
steps {
sh './scripts/run.py build'
}
}
stage('Run') {
when {
branch 'master'
}
steps {
sh './scripts/run.py push'
}
}
}steps
script
声明式pipeline是不能直接在steps块中写Groovy代码。 Jenkins pipeline专门提供了一个script步骤,你能在script步骤中像写代码一样写pipeline逻辑。
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
script {
result = sh (script: "git log -1|grep 'Release'", returnStatus: true)
echo "result: ${result}"
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
script {
result = sh (script: "git log -1|grep 'Release'", returnStatus: true)
echo "result: ${result}"
}
}
}
}
}script 步骤需要 [scripted-pipeline]块并在声明式流水线中执行。对于大多数用例来说,应该声明式流水线中的“脚本”步骤是不必要的,但是它可以提供一个有用的”逃生出口”。非平凡的规模和/或复杂性的script块应该被转移到 共享库 。
示例:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
script {
def browsers = ['chrome', 'firefox']
for (int i = 0; i < browsers.size(); ++i) {
echo "Testing the ${browsers[i]} browser"
}
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
script {
def browsers = ['chrome', 'firefox']
for (int i = 0; i < browsers.size(); ++i) {
echo "Testing the ${browsers[i]} browser"
}
}
}
}
}
}| 命令名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| error | 抛出异常,中断整个pipeline |
| timeout | timeout闭包内运行的步骤超时时间 |
| waitUntil | 一直循环运行闭包内容,直到return true,经常与timeout同时使用 |
| retry | 闭包内脚本重复执行次数 |
| sleep | 暂停pipeline一段时间,单位为秒 |
真正的执行语句是放在 steps 里的,这里可以包括许多 预先定义好的 step , 这里列出一些常用的
steps {
echo 'debugging'
sleep 120, unit: 'DAYS'
retry 3
error() //
dir // 指定工作目录
readFile
fileExists
withEnv
script
}steps {
echo 'debugging'
sleep 120, unit: 'DAYS'
retry 3
error() //
dir // 指定工作目录
readFile
fileExists
withEnv
script
}- 文件目录相关步骤
deleteDir 删除当前目录,它是一个无参步骤,删除的是当前工作目录。通常它与
dir步骤一起使用,用于删除指定目录下的内容。dir 切换到目录。默认
pipeline工作在工作空间目录下,dir步骤可以让我们切换到其它目录。例如:dir("/var/logs") { deleteDir() }dir("/var/logs") { deleteDir() }fileExists 判断文件是否存在。
fileExists('/tmp/a.jar')判断/tmp/a.jar文件是否存在。如果参数是相对路径,则判断在相对当前工作目录下,该文件是否存在。结果返回布尔类型。isUnix 判断是否为类
Unix系统。如果当前pipeline运行在一个类Unix系统上,则返回true。pwd 确认当前目录。
pwd与Linux的pwd命令一样,返回当前所在目录。它有一个布尔类型的可选参数:tmp,如果参数值为true,则返回与当前工作空间关联的临时目录。writeFile 将内容写入指定文件中。
writeFile支持的参数有: file:文件路径,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。 text:要写入的文件内容。 encoding(可选):目标文件的编码。如果留空,则使用操作系统默认的编码。如果写的是Base64的数据,则可以使用Base64编码。
- readFile:读取指定文件的内容,以文本返回。
readFile支持的参数有: file:路径,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。 encoding(可选):读取文件时使用的编码。
script {
// "amVua2lucyBib29r" 是"jenkins book"进行Base64编码后的值
writeFile(file: "base64File", text: "amVua2lucyBib29r", encoding: "Base64")
def content = readFile(file: "base64File", encoding: "UTF-8")
echo "${content}"
// 打印结果: jenkins book
}script {
// "amVua2lucyBib29r" 是"jenkins book"进行Base64编码后的值
writeFile(file: "base64File", text: "amVua2lucyBib29r", encoding: "Base64")
def content = readFile(file: "base64File", encoding: "UTF-8")
echo "${content}"
// 打印结果: jenkins book
}waitUntil
pipeline{
agent any
stages{
stage('stash'){
steps{
timeout(50){
waitUntil{
script{
def r = sh script: 'curl http://xxx', returnStatus: true
return (r == 0)
}
}
}
retry(10){
script{
sh script: 'curl http://xxx', returnStatus: true
}
}
sleep(20)
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo "结束job"
}
}
}pipeline{
agent any
stages{
stage('stash'){
steps{
timeout(50){
waitUntil{
script{
def r = sh script: 'curl http://xxx', returnStatus: true
return (r == 0)
}
}
}
retry(10){
script{
sh script: 'curl http://xxx', returnStatus: true
}
}
sleep(20)
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo "结束job"
}
}
}post
post 用于后处理,位于 pipeline 顶级或者 stage 内部。当一定场景满足后,执行条件块内的 steps
post 支持的 steps 和 stages 里的 steps 相同。下面是各种常用的场景:
| 条件 | 执行场合 |
|---|---|
| always | 总是执行 |
| success | 前面的 stage 全部成功时执行;如果 post 位于 stage 内部,则是 stage 成功时执行 |
| failure | 前面的 stage 有失败时执行;如果 post 位于 stage 内部,则是 stage 失败时执行 |
| changed | 只有当流水线或者阶段完成状态与之前不同时 |
| unstable | 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为“unstable”运行。列入:测试失败 |
| aborted | 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为“aborted”运行。列如:手动取消 |
Jenkinsfile (Declarative Pipeline)
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'I will always say Hello again!'
}
}
}Jenkinsfile (Declarative Pipeline)
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'I will always say Hello again!'
}
}
}嵌套执行结构
stage 下又可以嵌套 stages,继续向下嵌套多个 stage,呈顺序执行。
并行执行结构
声明式流水线的阶段可以在他们内部声明多隔嵌套阶段, 它们将并行执行。 注意,一个阶段必须只有一个 steps 或 parallel的阶段。 嵌套阶段本身不能包含 进一步的 parallel 阶段, 但是其他的阶段的行为与任何其他 stageparallel的阶段不能包含 agent 或 tools阶段, 因为他们没有相关 steps。
另外, 通过添加 failFast true 到包含parallel的 stage中, 当其中一个进程失败时,你可以强制所有的 parallel 阶段都被终止
一个 stage 可以声明为多个 stage 的并行执行,只要再加一层 parallel 指令,parallel 内的各个 stage 将并行执行,但是内部不能继续嵌套 parallel。基本结构为:
stages {
stage('Parallel Stage') {
parallel {
stage('Branch A') {
...
}
stage('Branch B') {
...
}
stage('Branch C') {
...
}
}
}
}stages {
stage('Parallel Stage') {
parallel {
stage('Branch A') {
...
}
stage('Branch B') {
...
}
stage('Branch C') {
...
}
}
}
}但是由于 pipeline 文件本身是 Groovy 代码,所以并没有规定在 pipeline {} 以外不允许有 Groovy代码。正相反,额外的辅助代码,可以带来更多更灵活的功能
pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Run Tests') {
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Test On Chrome') {
agent { label "chrome" }
steps {
echo "Chrome UI测试"
}
}
stage("Test On Firefox") {
agent { label "firefox" }
steps {
echo "Firefox UI测试"
}
}
stage("Test On IE") {
agent { label "ie" }
steps {
echo "IE UI测试"
}
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent none
stages {
stage('Run Tests') {
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Test On Chrome') {
agent { label "chrome" }
steps {
echo "Chrome UI测试"
}
}
stage("Test On Firefox") {
agent { label "firefox" }
steps {
echo "Firefox UI测试"
}
}
stage("Test On IE") {
agent { label "ie" }
steps {
echo "IE UI测试"
}
}
}
}
}
}示例:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Non-Parallel Stage') {
steps {
echo 'This stage will be executed first.'
}
}
stage('Parallel Stage') {
when {
branch 'master'
}
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Branch A') {
agent {
label "for-branch-a"
}
steps {
echo "On Branch A"
}
}
stage('Branch B') {
agent {
label "for-branch-b"
}
steps {
echo "On Branch B"
}
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Non-Parallel Stage') {
steps {
echo 'This stage will be executed first.'
}
}
stage('Parallel Stage') {
when {
branch 'master'
}
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Branch A') {
agent {
label "for-branch-a"
}
steps {
echo "On Branch A"
}
}
stage('Branch B') {
agent {
label "for-branch-b"
}
steps {
echo "On Branch B"
}
}
}
}
}
}3.编写规范
4.判断语句
4.1if
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('flow control') {
steps {
script {
if ( 10 == 10) {
println "pass"
}else {
println "failed"
}
}
}
}
}
}
#案例
stage('deploy service') {
steps {
sshagent(credentials: ['online-mq']) {
//sh "ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ${HOST_TEST} uname -a"
//--exclude=appsettings.json
sh '''
if [ "${HOST_TEST}" == "172" ];then
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
rsync -avzP --exclude=appsettings.json ${SOURCE_DIR_taskWeb}/* ${HOST_TEST}:${TARGET_DIR_taskWeb}
elif [ "${HOST_TEST}" == "172" ];then
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
rsync -avzP --exclude=appsettings.json ${SOURCE_DIR_taskWeb}/* ${HOST_TEST}:${TARGET_DIR_taskWeb}
else
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
exit 0
fi
'''
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('flow control') {
steps {
script {
if ( 10 == 10) {
println "pass"
}else {
println "failed"
}
}
}
}
}
}
#案例
stage('deploy service') {
steps {
sshagent(credentials: ['online-mq']) {
//sh "ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ${HOST_TEST} uname -a"
//--exclude=appsettings.json
sh '''
if [ "${HOST_TEST}" == "172" ];then
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
rsync -avzP --exclude=appsettings.json ${SOURCE_DIR_taskWeb}/* ${HOST_TEST}:${TARGET_DIR_taskWeb}
elif [ "${HOST_TEST}" == "172" ];then
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
rsync -avzP --exclude=appsettings.json ${SOURCE_DIR_taskWeb}/* ${HOST_TEST}:${TARGET_DIR_taskWeb}
else
echo "${HOST_TEST} is not "
exit 0
fi
'''
}
}
}4.2 case
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Case lab') {
steps {
echo 'This stage will be executed first.'
script{
switch("$contraller"){
case "Job1":
println "This is Job1"
break
case "Job2":
println "This is Job2"
break
case "Job3":
println "This is Job3"
break
default:
echo "############ wrong Job name ############"
break
}
}
}
}
}
}pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Case lab') {
steps {
echo 'This stage will be executed first.'
script{
switch("$contraller"){
case "Job1":
println "This is Job1"
break
case "Job2":
println "This is Job2"
break
case "Job3":
println "This is Job3"
break
default:
echo "############ wrong Job name ############"
break
}
}
}
}
}
}5.变量
Jenkins Pipeline通过全局变量公开环境变量
1.自定义变量(局部)
def username = 'jenkins'
echo "hello Mr.${username}"def username = 'jenkins'
echo "hello Mr.${username}"2.环境变量
withEnv(['JAVA_HOME=/data/jdk']) {
sh '$JAVA_HOME/bin/start.sh'
}withEnv(['JAVA_HOME=/data/jdk']) {
sh '$JAVA_HOME/bin/start.sh'
}3.环境变量(全局)
environment {
JAVA_HOME='/data/jdk'
}
echo " java path $JAVA_HOME"environment {
JAVA_HOME='/data/jdk'
}
echo " java path $JAVA_HOME"4.参数化构建(全局)
parameters {
string(name: 'GIT_BRANCH', defaultValue: 'master', description: 'default build branch')
}
调用:
echo "${params.name}"parameters {
string(name: 'GIT_BRANCH', defaultValue: 'master', description: 'default build branch')
}
调用:
echo "${params.name}"6.FAQ
没有找到相关的环境变量, 这个是我们在parameters中引用了流水线中的变量导致的,可能因为加载顺序不同导致的,解决方法是可以在pipeline{} 外部定义变量进行引用
roovy.lang.MissingPropertyException: No such property: DEPLOY_DESC for class: groovy.lang.Binding
at groovy.lang.Binding.getVariable(Binding.java:63)roovy.lang.MissingPropertyException: No such property: DEPLOY_DESC for class: groovy.lang.Binding
at groovy.lang.Binding.getVariable(Binding.java:63)