1.systemd简介
systemd 是一个 Linux 系统基础组件的集合,提供了一个系统和服务管理器,运行为 PID 1 并负责启动其它程序。功能包括:支持并行化任务;同时采用 socket 式与 D-Bus 总线式启用服务;按需启动守护进程(daemon);利用 Linux 的 cgroups 监视进程;支持快照和系统恢复;维护挂载点和自动挂载点;各服务间基于依赖关系进行精密控制。systemd 支持 SysV 和 LSB 初始脚本,可以替代 sysvinit。除此之外,功能还包括日志进程、控制基础系统配置,维护登陆用户列表以及系统账户、运行时目录和设置,可以运行容器和虚拟机,可以简单的管理网络配置、网络时间同步、日志转发和名称解析等。
以前启动方式:
不同系统的init版本
centos5: Sysv Init
centos6: Upstart
centos7: systemdcentos5: Sysv Init
centos6: Upstart
centos7: systemdsystemd 设计目标
- 改进效能。使用二进制代码替换松散的 SYSV 启动脚本,减少频繁的进程创建,库加载,内核/用户切换。
- 利用 Dbus 进程间通讯与 socket 激活机制,解决任务启动时的依赖问题,实现启动并行化。
- 实现任务(daemons)的精确控制。使用内核的 cgroup 机制,不依赖 pid 来追踪进程,即使是两次 fork 之后生成的守护进程也不会脱离 systemd 的控制。
- 统一任务定义。用户不需要自行编写 shell 脚本,而仅依据 systemd 制定的 unit 规则
systemd 体系架构
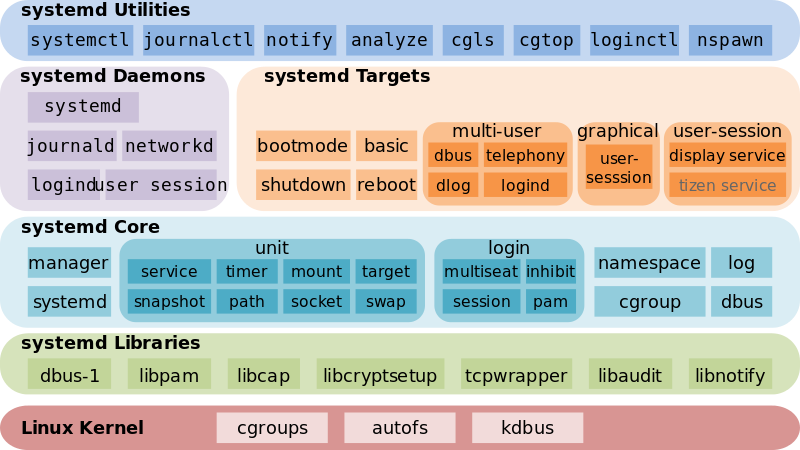
- 最底层:systemd 内核层面依赖 cgroup、autofs、kdbus
- 第二层:systemd libraries 是 systemd 依赖库
- 第三层:systemd Core 是 systemd 自己的库
- 第四层:systemd daemons 以及 targets 是自带的一些基本 unit、target,类似于 sysvinit 中自带的脚本
- 最上层就是和 systemd 交互的一些工具
2.systemd单元文件位置
| 目录 | 描述 |
|---|---|
/usr/lib/systemd/system/ | Systemd 单元文件随已安装的 RPM 软件包一起分发。 |
/run/systemd/system/ | 在运行时创建的 Systemd 单元文件。此目录优先于已安装服务单元文件的目录。 |
/etc/systemd/system/ | Systemd 创建的单元文件systemctl enable以及为扩展服务而添加的单元文件。该目录优先于包含运行时单元文件的目录。 |
systemd默认从 /etc/systemd/system/ 目录读取配置文件
centos7的服务脚本一般存放在 /usr/lib/systemd 下,有系统 system 和 user 区分。 即 /usr/lib/systemd/system 和 /usr/lib/systemd/user
三个目录的文件优先级依次从低到高,同一服务三个地方都配置了,优先级高的会覆盖优先级低的
/run/systemd/system 是进程在运行时动态创建unit文件的目录,一般很少修改,除非是修改程序运行时的一些参数时,即Session级别的,才在这里做修改
systemd 的默认配置是在编译期间定义的,可以在 systemd 配置文件中找到/etc/systemd/system.conf
3.Unit服务配置
3.1运行级别
| 运行级别 | 目标单位 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
0 | runlevel0.target,poweroff.target | 关闭并关闭系统电源。 |
1 | runlevel1.target,rescue.target | 设置救援外壳。 |
2 | runlevel2.target,multi-user.target | 设置非图形多用户系统。 |
3 | runlevel3.target,multi-user.target | 设置非图形多用户系统。 |
4 | runlevel4.target,multi-user.target | 设置非图形多用户系统。 |
5 | runlevel5.target,graphical.target | 设置图形多用户系统。 |
6 | runlevel6.target,reboot.target | 关闭并重新启动系统 |
3.2文件结构
一般会分为3部分
[Unit]
[Service]
[Install][Unit]
[Service]
[Install]- Unit 和 Install 段:所有 Unit 文件通用,用于配置服务(或其它系统资源)的描述、依赖和随系统启动的方式
- Service 段:服务(Service)类型的 Unit 文件(后缀为 .service)特有的,用于定义服务的具体管理和操作方法
- Install 段:所有 Unit 文件通用,用来定义如何启动,以及是否开机启动
❌ 注意
单元文件中的区段名和字段名大小写敏感, 每个区段内都是一些等号连接的键值对(键值对的等号两侧不能有空格)
Unit
查看完整参数,man systemd.unit
或者在线查看
https://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/systemd.resource-control.5.html
Option section, see the systemd.unit(5) manual page | Description |
|---|---|
Description | A meaningful description of the unit. This text is displayed for example in the output of the systemctl status command. |
Documentation | Provides a list of URIs referencing documentation for the unit. |
After | Defines the order in which units are started. The unit starts only after the units specified in After are active. Unlike Requires, After does not explicitly activate the specified units. The Before option has the opposite functionality to After. |
| Requires | Configures dependencies on other units. The units listed in Requires are activated together with the unit. If any of the required units fail to start, the unit is not activated. |
| Wants | Configures weaker dependencies than Requires. If any of the listed units does not start successfully, it has no impact on the unit activation. This is the recommended way to establish custom unit dependencies. |
| Conflicts | Configures negative dependencies, an opposite to Requires. |
Service
Option section, see the systemd.service(5) manual page | Description |
|---|---|
Type | Configures the unit process startup type that affects the functionality of ExecStart and related options. One of:* simple – The default value. The process started with ExecStart is the main process of the service.* forking – The process started with ExecStart spawns a child process that becomes the main process of the service. The parent process exits when the startup is complete.* oneshot – This type is similar to simple, but the process exits before starting consequent units.* dbus – This type is similar to simple, but consequent units are started only after the main process gains a D-Bus name.* notify – This type is similar to simple, but consequent units are started only after a notification message is sent via the sd_notify() function.* idle – similar to simple, the actual execution of the service binary is delayed until all jobs are finished, which avoids mixing the status output with shell output of services. |
ExecStart | Specifies commands or scripts to be executed when the unit is started. ExecStartPre and ExecStartPost specify custom commands to be executed before and after ExecStart. Type=oneshot enables specifying multiple custom commands that are then executed sequentially. |
ExecStop | Specifies commands or scripts to be executed when the unit is stopped. |
ExecReload | Specifies commands or scripts to be executed when the unit is reloaded. |
Restart | With this option enabled, the service is restarted after its process exits, with the exception of a clean stop by the systemctl command. |
RemainAfterExit | If set to True, the service is considered active even when all its processes exited. Default value is False. This option is especially useful if Type=oneshot is configured. |
| User | |
| Group | |
| LimitCORE | LimitCORE=infinity:限制内核文件的大小 |
| LimitNOFILE | LimitNOFILE=65536:服务最大允许打开的文件描述符数量 |
| LimitNPROC | LimitNPROC=65536:进程的最大数量 |
| Environment | Environment="export JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk" ,可以写多行 |
Install
Alias | Provides a space-separated list of additional names for the unit. Most systemctl commands, excluding systemctl enable, can use aliases instead of the actual unit name. |
|---|---|
RequiredBy | A list of units that depend on the unit. When this unit is enabled, the units listed in RequiredBy gain a Require dependency on the unit. |
WantedBy | A list of units that weakly depend on the unit. When this unit is enabled, the units listed in WantedBy gain a Want dependency on the unit. |
Also | Specifies a list of units to be installed or uninstalled along with the unit. |
DefaultInstance | Limited to instantiated units, this option specifies the default instance for which the unit is enabled. |
- 案例
touch /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
chmod 644 /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
[Unit]
Description=containerd container runtime
Documentation=https://containerd.io
After=network.target local-fs.target
[Service]
ExecStartPre=-/sbin/modprobe overlay
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/containerd
Type=notify
Delegate=yes
KillMode=process
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
# Having non-zero Limit*s causes performance problems due to accounting overhead
# in the kernel. We recommend using cgroups to do container-local accounting.
LimitNPROC=infinity
LimitCORE=infinity
LimitNOFILE=1048576
# Comment TasksMax if your systemd version does not supports it.
# Only systemd 226 and above support this version.
TasksMax=infinity
OOMScoreAdjust=-999
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targettouch /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
chmod 644 /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service
[Unit]
Description=containerd container runtime
Documentation=https://containerd.io
After=network.target local-fs.target
[Service]
ExecStartPre=-/sbin/modprobe overlay
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/containerd
Type=notify
Delegate=yes
KillMode=process
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
# Having non-zero Limit*s causes performance problems due to accounting overhead
# in the kernel. We recommend using cgroups to do container-local accounting.
LimitNPROC=infinity
LimitCORE=infinity
LimitNOFILE=1048576
# Comment TasksMax if your systemd version does not supports it.
# Only systemd 226 and above support this version.
TasksMax=infinity
OOMScoreAdjust=-999
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target4.资源管理
4.1 Unit管理
- 查看当前系统的所有 Unit
# 列出正在运行的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units
# 列出所有Unit,包括没有找到配置文件的或者启动失败的
$ systemctl list-units --all
# 列出所有没有运行的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --all --state=inactive
# 列出所有加载失败的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --failed
# 列出所有正在运行的、类型为 service 的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --type=service
# 查看 Unit 配置文件的内容
$ systemctl cat docker.service# 列出正在运行的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units
# 列出所有Unit,包括没有找到配置文件的或者启动失败的
$ systemctl list-units --all
# 列出所有没有运行的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --all --state=inactive
# 列出所有加载失败的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --failed
# 列出所有正在运行的、类型为 service 的 Unit
$ systemctl list-units --type=service
# 查看 Unit 配置文件的内容
$ systemctl cat docker.service- 查看 Unit 的状态
# 显示系统状态
$ systemctl status
# 显示单个 Unit 的状态
$ ystemctl status bluetooth.service
# 显示远程主机的某个 Unit 的状态
$ systemctl -H root@rhel7.example.com status httpd.service# 显示系统状态
$ systemctl status
# 显示单个 Unit 的状态
$ ystemctl status bluetooth.service
# 显示远程主机的某个 Unit 的状态
$ systemctl -H root@rhel7.example.com status httpd.service- 启动和加载服务
# 立即启动一个服务
$ sudo systemctl start apache.service
# 立即停止一个服务
$ sudo systemctl stop apache.service
# 重启一个服务
$ sudo systemctl restart apache.service
# 杀死一个服务的所有子进程
$ sudo systemctl kill apache.service
# 重新加载一个服务的配置文件
$ sudo systemctl reload apache.service
# 重载所有修改过的配置文件
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 显示某个 Unit 的所有底层参数
$ systemctl show docker.service
# 显示某个 Unit 的指定属性的值
$ systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
# 设置某个 Unit 的指定属性
$ sudo systemctl set-property httpd.service CPUShares=500# 立即启动一个服务
$ sudo systemctl start apache.service
# 立即停止一个服务
$ sudo systemctl stop apache.service
# 重启一个服务
$ sudo systemctl restart apache.service
# 杀死一个服务的所有子进程
$ sudo systemctl kill apache.service
# 重新加载一个服务的配置文件
$ sudo systemctl reload apache.service
# 重载所有修改过的配置文件
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 显示某个 Unit 的所有底层参数
$ systemctl show docker.service
# 显示某个 Unit 的指定属性的值
$ systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
# 设置某个 Unit 的指定属性
$ sudo systemctl set-property httpd.service CPUShares=500- 查看依赖关系
# 列出一个 Unit 的所有依赖,默认不会列出 target 类型
$ systemctl list-dependencies nginx.service
# 列出一个 Unit 的所有依赖,包括 target 类型
$ systemctl list-dependencies --all nginx.service# 列出一个 Unit 的所有依赖,默认不会列出 target 类型
$ systemctl list-dependencies nginx.service
# 列出一个 Unit 的所有依赖,包括 target 类型
$ systemctl list-dependencies --all nginx.service4.2系统管理命令
systemctl是 Systemd 的主命令,用于管理系统
# 重启系统
$ systemctl reboot
# 关闭系统,切断电源
$ systemctl poweroff
# CPU停止工作
$ systemctl halt
# 暂停系统
$ systemctl suspend
# 让系统进入冬眠状态
$ systemctl hibernate
# 让系统进入交互式休眠状态
$ systemctl hybrid-sleep
# 启动进入救援状态(单用户状态)
$ systemctl rescue# 重启系统
$ systemctl reboot
# 关闭系统,切断电源
$ systemctl poweroff
# CPU停止工作
$ systemctl halt
# 暂停系统
$ systemctl suspend
# 让系统进入冬眠状态
$ systemctl hibernate
# 让系统进入交互式休眠状态
$ systemctl hybrid-sleep
# 启动进入救援状态(单用户状态)
$ systemctl rescue4.3启动过程
当内核加载到内存中后开始执行 systemd 。根据 dmesg 的日志我们可以了解到 systemd 启动后执行了哪一些操作
[ 2.516258] Run /sbin/init as init process
[ 3.992535] systemd[1]: systemd 237 running in system mode. (+PAM +AUDIT +SELINUX +IMA +APPARMOR +SMACK +SYSVINIT +UTMP +LIBCRYPTSETUP +GCRYPT +GNUTLS +ACL +XZ +LZ4 +SECCOMP +BLKID +ELFUTILS +KMOD -IDN2 +IDN -PCRE2 default-hierarchy=hybrid)
[ 4.002297] systemd[1]: Detected virtualization kvm.
[ 4.004593] systemd[1]: Detected architecture x86-64.
[ 4.031531] systemd[1]: Set hostname to <blog>.
[ 5.343604] systemd[1]: Reached target Swap.
[ 5.355156] systemd[1]: Started Dispatch Password Requests to Console Directory Watch.
[ 5.367360] systemd[1]: Created slice User and Session Slice.
[ 5.379321] systemd[1]: Set up automount Arbitrary Executable File Formats File System Automount Point.
[ 5.395189] systemd[1]: Started Forward Password Requests to Wall Directory Watch.
[ 5.411078] systemd[1]: Reached target Local Encrypted Volumes.
[ 5.644759] EXT4-fs (sda1): re-mounted. Opts: (null)
[ 5.702603] RPC: Registered named UNIX socket transport module.
[ 5.704115] RPC: Registered udp transport module.
[ 5.705318] RPC: Registered tcp transport module.
[ 5.706573] RPC: Registered tcp NFSv4.1 backchannel transport module.
[ 5.825727] Loading iSCSI transport class v2.0-870.
[ 5.912079] iscsi: registered transport (tcp)
[ 5.942499] systemd-journald[196]: Received request to flush runtime journal from PID 1
[ 5.973269] systemd-journald[196]: File /var/log/journal/7bc72ce3e0aa559e38159aa4fa0547f9/system.journal corrupted or uncleanly shut down, renaming and replacing.[ 2.516258] Run /sbin/init as init process
[ 3.992535] systemd[1]: systemd 237 running in system mode. (+PAM +AUDIT +SELINUX +IMA +APPARMOR +SMACK +SYSVINIT +UTMP +LIBCRYPTSETUP +GCRYPT +GNUTLS +ACL +XZ +LZ4 +SECCOMP +BLKID +ELFUTILS +KMOD -IDN2 +IDN -PCRE2 default-hierarchy=hybrid)
[ 4.002297] systemd[1]: Detected virtualization kvm.
[ 4.004593] systemd[1]: Detected architecture x86-64.
[ 4.031531] systemd[1]: Set hostname to <blog>.
[ 5.343604] systemd[1]: Reached target Swap.
[ 5.355156] systemd[1]: Started Dispatch Password Requests to Console Directory Watch.
[ 5.367360] systemd[1]: Created slice User and Session Slice.
[ 5.379321] systemd[1]: Set up automount Arbitrary Executable File Formats File System Automount Point.
[ 5.395189] systemd[1]: Started Forward Password Requests to Wall Directory Watch.
[ 5.411078] systemd[1]: Reached target Local Encrypted Volumes.
[ 5.644759] EXT4-fs (sda1): re-mounted. Opts: (null)
[ 5.702603] RPC: Registered named UNIX socket transport module.
[ 5.704115] RPC: Registered udp transport module.
[ 5.705318] RPC: Registered tcp transport module.
[ 5.706573] RPC: Registered tcp NFSv4.1 backchannel transport module.
[ 5.825727] Loading iSCSI transport class v2.0-870.
[ 5.912079] iscsi: registered transport (tcp)
[ 5.942499] systemd-journald[196]: Received request to flush runtime journal from PID 1
[ 5.973269] systemd-journald[196]: File /var/log/journal/7bc72ce3e0aa559e38159aa4fa0547f9/system.journal corrupted or uncleanly shut down, renaming and replacing.local-fs-pre.target
|
v
(various mounts and (various swap (various cryptsetup
fsck services...) devices...) devices...) (various low-level (various low-level
| | | services: udevd, API VFS mounts:
v v v tmpfiles, random mqueue, configfs,
local-fs.target swap.target cryptsetup.target seed, sysctl, ...) debugfs, ...)
| | | | |
\__________________|_________________ | `_______________` |____________________/
\|/
v
sysinit.target
|
`________________________________` /|\________________________________________
/ | | | \
| | | | |
v v | v v
(various (various | (various rescue.service
timers...) paths...) | sockets...) |
| | | | v
v v | v *rescue.target
timers.target paths.target | sockets.target
| | | |
v \_________________ | `_______________` /
\|/
v
basic.target
|
`________________________________` /| emergency.service
/ | | |
| | | v
v v v *emergency.target
display- (various system (various system
manager.service services services)
| required for |
| graphical UIs) v
| | *multi-user.target
| | |
\_________________ | `_____________` /
\|/
v
*graphical.targetlocal-fs-pre.target
|
v
(various mounts and (various swap (various cryptsetup
fsck services...) devices...) devices...) (various low-level (various low-level
| | | services: udevd, API VFS mounts:
v v v tmpfiles, random mqueue, configfs,
local-fs.target swap.target cryptsetup.target seed, sysctl, ...) debugfs, ...)
| | | | |
\__________________|_________________ | `_______________` |____________________/
\|/
v
sysinit.target
|
`________________________________` /|\________________________________________
/ | | | \
| | | | |
v v | v v
(various (various | (various rescue.service
timers...) paths...) | sockets...) |
| | | | v
v v | v *rescue.target
timers.target paths.target | sockets.target
| | | |
v \_________________ | `_______________` /
\|/
v
basic.target
|
`________________________________` /| emergency.service
/ | | |
| | | v
v v v *emergency.target
display- (various system (various system
manager.service services services)
| required for |
| graphical UIs) v
| | *multi-user.target
| | |
\_________________ | `_____________` /
\|/
v
*graphical.target- systemd 执行的第一个目标是 default.target。但实际上 default.target 是指向 graphical.target 的软链接。Graphical.target 的实际位置是
/usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target
cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.targetcat /usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target- 在 default.target 这个阶段,会启动 multi-user.target 而这个 target 将自己的子单元放在目录
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants里。这个 target 为多用户支持设定系统环境。非 root 用户会在这个阶段的引导过程中启用。防火墙相关的服务也会在这个阶段启动。multi-user.target 会将控制权交给另一层 basic.target
cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.targetcat /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target- basic.target 单元用于启动普通服务特别是图形管理服务。它通过
/etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants目录来决定哪些服务会被启动,basic.target 之后将控制权交给 sysinit.target.
tree /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wantstree /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants- sysinit.target 会启动重要的系统服务例如系统挂载,内存交换空间和设备,内核补充选项等等。sysinit.target 在启动过程中会传递给 local-fs.target
tree /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wantstree /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wantslocal-fs.target,这个 target 单元不会启动用户相关的服务,它只处理底层核心服务。这个 target 会根据 /etc/fstab 和 /etc/inittab 来执行相关操作
cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sysinit.target cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sysinit.target5.systemctl 与 service 命令的区别
- systemctl 融合了 service 和 chkconfig 的功能
- service 命令实际上重定向到 systemctl 命令
Target 与 SysV-init 进程的主要区别:
- 默认的 RunLevel(在 /etc/inittab 文件设置)现在被默认的 Target 取代,位置是 /etc/systemd/system/default.target,通常符号链接到graphical.target(图形界面)或者multi-user.target(多用户命令行)。
- 启动脚本的位置,以前是 /etc/init.d 目录,符号链接到不同的 RunLevel 目录 (比如 /etc/rc3.d、/etc/rc5.d 等),现在则存放在 /lib/systemd/system 和 /etc/systemd/system 目录。
- 配置文件的位置,以前 init 进程的配置文件是 /etc/inittab,各种服务的配置文件存放在 /etc/sysconfig 目录。现在的配置文件主要存放在 /lib/systemd 目录,在 /etc/systemd 目录里面的修改可以覆盖原始设置